ACIDS, BASES, & SALTS
1. Acid: - An acid is defined as a substance whose water solution tastes sour, turns blue litmus red, and neutralizes bases. example- lactic, citric, Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), etc.2. Base: - A substance is called base if its aqueous solution tastes bitter, turns red litmus blue, or neutralizes acids. example- Baking soda, bleach, NaOH, KOH, etc.
3. Salt: - Salt is a neutral substance whose aqueous solution does not affect litmus. example- Sodium chloride (NaCl), Potassium chloride (KCl), etc.
What is litmus paper?
1. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ACID AND BASES
Chemical Properties of Acid and Bases
1. Reactions of Acids and Bases with Metals
2. The Reaction of Metal Carbonates/Metal Bicarbonates with Acids
Metal carbonates/metal bicarbonates react with acids to produce salt, carbon dioxide, and water. For example
3. The Reaction of Metal Oxide with Acids
Metal oxides react with acids to produce salt and water. For example
4. The Reaction of Non-metal Oxide with Bases
Non-metal oxides react with bases to produce salt and water. For example
5. The Reaction between Acids and Bases
Acids react with bases to produce salt and water. The reaction between acids and bases to give salts is known as the neutralization reaction. For example
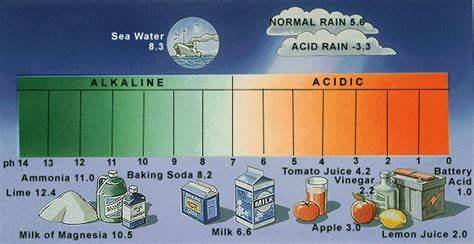
2. HOW STRONG ARE ACID OR BASE SOLUTIONS?
The amount of H+ present in a solution can be measured by using a universal indicator. It is a mixture of several indicators. It shows different colors at different concentrations of hydrogen ions. A pH scale is a scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
1. pH is measured from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline).
2. The strength of acids and bases depends on the number of H+ ions and OH– ions produced, respectively.
4. The pH of a neutral solution is 7.
5. The pH of an acidic solution is less than 7.
6. The pH of the basic solution is more than 7.
pH of some common substances shown on a paper
3. IMPORTANCE OF pH IN EVERYDAY LIFE
Sodium hydroxide: - When
electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called
brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. The process is called the
chlor-alkali process because of the products formed– chlor for chlorine and
alkali for sodium hydroxide.
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
+ Cl2 (g) + H2 (g)
Bleaching powder: - Bleaching
powder is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2
].
Ca (OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Baking soda: - The
chemical name of the compound is sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO3 ).
It is produced using sodium chloride as one of the raw materials.
NaCl
+ H2O + CO + NH3 → NH4 Cl + NaHCO3
Washing soda:
- Another chemical that can be obtained from sodium chloride is Na2CO3
.10H2O (washing soda). It is also a basic salt.
Na2CO3
+ 10 H2O → Na2CO3.10 H2O









Comments
Post a Comment